In this article i will talk about how we can transfer the data from

Controller to View or passing data between actions of a controller.Model
The best and recommended way to pass the data from a
Controller to View is by using Model classes. If we create a strongly typed view than that view is capable of accessing the object/model that is being passed to it from the controller.ViewModel
Now consider a scenario where we need to create a view which needs data from two or more classes/models. How can we create a strongly type view that can extract data from two models. The answer to this is that we cannot. But we can create a new class that can contain these classes' objects in it and this class can be passed as the model class to the view. Now this class is created to be used as model on some views. All such classes are called as
ViewModels.ViewData and ViewBag
To transfer small amount of data, we can use
Viewdata andViewBag.ViewBag comes with all the benefits of ViewData with an additional benefit that type casting is not required.TempData
Now the problem with all the above ways of data transfer was that the data is only alive for current request. The data is lost if a redirection takes place i.e. one Action redirects to another action. For the scenarios where we need to persist the data between actions/redirection another dictionary object called
TempData can be used. It is derived from TempDataDictionary. It is created on top of session. Its will live till the redirected view is fully loaded.Sessions
Session is the way to persist the data till the current session is alive. If we need some data to be accessible from multiple controllers, actions and views then Session is the way to store and retrieve the data.Model
Let us first see how we can create a strongly typed view which will display the data that is being passed to it from the controller. Lets have a simple Model like:
public class Book
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public string BookName { get; set; }
public string Author { get; set; }
public string ISBN { get; set; }
}
Now let us create a simple Action called
SampleBook and create a book object in it and then pass it on to the view.public ActionResult SampleBook()
{
Book book = new Book
{
ID = 1,
BookName = "Sample Book",
Author = "Sample Author",
ISBN = "Not available"
};
return View(book);
}
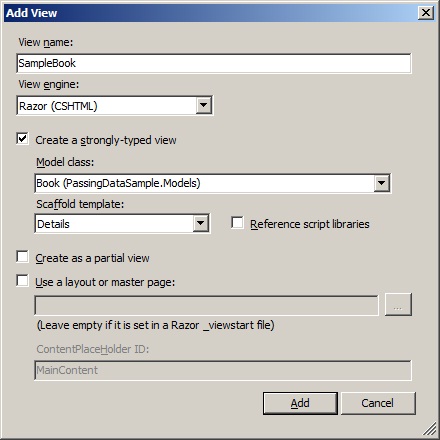
Now lets add a strongly typed View for this action which will use
Book model to retrieve the data. Lets also use the "Details" scaffold so that we don't have to write the code to access the data from the model(just for the demonstration purpose).
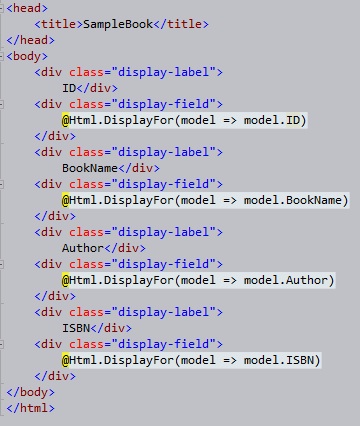
Now if we look at the code for the View we can see that the data is being extracted from the
Model which is an object of Book type passed from the controller.
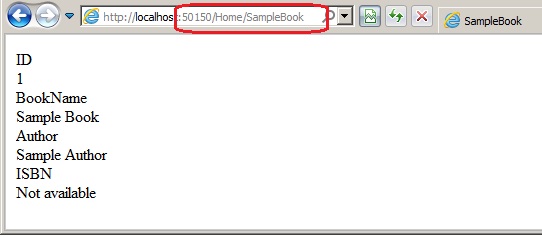
When we run the application:

ViewModel
Now let us say we need a View that should display the data from multiple models. Lets say we have one more class which is getting some custom message and it should be displayed on the page whenever a
Book data is being displayed. Now this message data is contained in a separate model as:public class Message
{
public string MessageText { get; set; }
public string MessageFrom { get; set; }
}
Now we need to pass two objects to the View one Book object and another
Message object. Now to do this we need to create a new class i.e. the ViewModel class which will contain these two object in it.public class ShowBookAndMessageViewModel
{
public Book Book { get; set; }
public Message Message {get;set;}
}
Now let is create one more action in our controller. This action will create this
ViewModel object and pass it to the view.public ActionResult SampleBook2()
{
Book book = new Book
{
ID = 1,
BookName = "Sample Book",
Author = "Sample Author",
ISBN = "Not available"
};
Message msg = new Message
{
MessageText = "This is a Sample Message",
MessageFrom = "Test user"
};
ShowBookAndMessageViewModel viewModel = new ShowBookAndMessageViewModel
{
Message = msg,
Book = book
};
return View(viewModel);
}
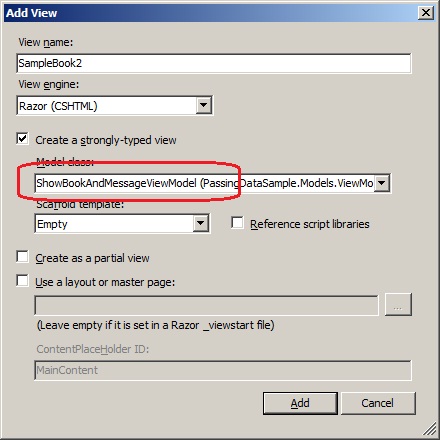
Now let us create a strongly typed view that will use this
ViewModel class to extract the data.
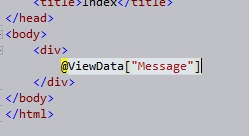
And now let us see the code that we need to extract the data from this
ViewModel and show it on the View.
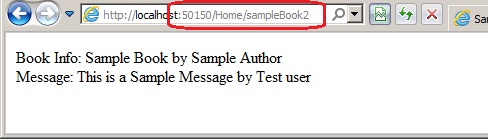
And when we run the application we can see that data can be extracted from this
ViewModel class and then corresponding data from Book and Message class and be extracted and shown on the View.
ViewData
We have discussed that the
ViewData can be used to pass simple and small data from controller to the view Let is see how we can pass a simple message string from Controller to View using ViewData.public ActionResult Index()
{
ViewData["Message"] = "This Message is coming from ViewData";
return View();
}
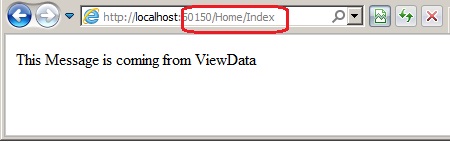
And now this data can be extracted from the view as:

And when we run the application:

Note: We are not type casting the data in view because it is simple string. If this data would have been of some complex type, type casting would become inevitable.
ViewBag
Now let us try to implement the same functionality like above but by using
ViewBag instead of ViewData.public ActionResult Index2()
{
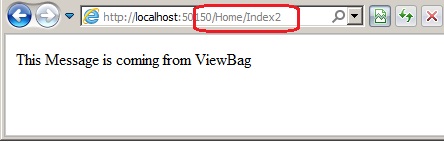
ViewBag.Message = "This Message is coming from ViewBag";
return View();
}
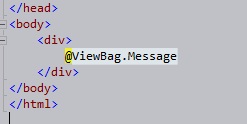
And now this data can be extracted from the view as:

And when we run the application:

TempData
Now let us say we have an action method redirect to another action method and we need to pass some data from one action method to another action method. To do this you we will have to use
TempData.public ActionResult SampleBook3()
{
Book book = new Book
{
ID = 1,
BookName = "Sample Book",
Author = "Sample Author",
ISBN = "Not available"
};
TempData["BookData"] = book;
return RedirectToAction("SampleBook4");
}
public ActionResult SampleBook4()
{
Book book = TempData["BookData"] as Book;
return View(book);
}
Now when the
SampleBook3 action will be called it will create a Book type, put it in a TempData variable and then redirect to action SampleBook4. Now in SampleBook4, the data will be extracted from theTempData and then the View for the SampleBook4 will be shown which is a strongly typed view and is capable of showing the data from the Book model.Session
Use of sessions has nothing new for the the web developers. We can use session variables to persist the data for a complete session. To demonstrate this let us implement the above functionality using sessions instead of
TempData.public ActionResult SampleBook5()
{
Book book = new Book
{
ID = 1,
BookName = "Sample Book",
Author = "Sample Author",
ISBN = "Not available"
};
Session["BookData"] = book;
return RedirectToAction("SampleBook6");
}
public ActionResult SampleBook6()
{
Book book = Session["BookData"] as Book;
return View(book);
}
Now when the
SampleBook5 action will be called it will create a Book type, put it in a session variable and then redirect to action SampleBook6. Now in SampleBook6, the data will be extracted from the Session and then the View for the SampleBook6 will be shown which is a strongly typed view and is capable of showing the data from the Book model.Note: The sample application contains complete application demonstrating all the techniques. Please refer to the sample application for better understanding.
Point of interest
In this article we saw various ways of passing the data between controllers and view and between action in a controller.





